Smart Agriculture
Smart agriculture integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and data analytics to optimize farming practices and enhance productivity. By using sensors, drones, and automated systems, farmers can monitor soil health, weather conditions, and crop growth in real time. This data-driven approach allows for precision in resource management, such as water and fertilizer use, reducing waste and improving sustainability. Ultimately, smart agriculture aims to increase yields, reduce environmental impact, and ensure food security.
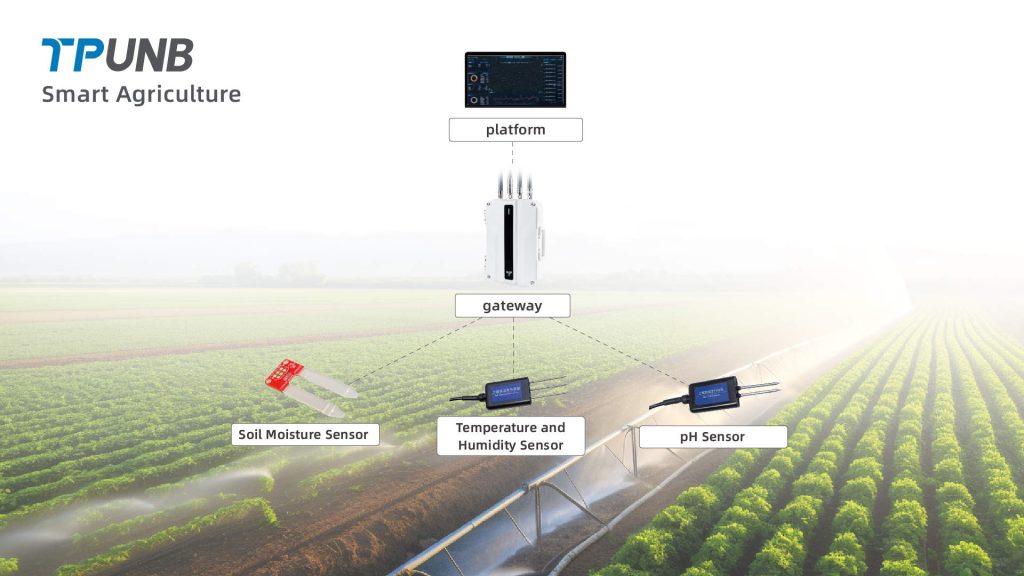
Advantages of TPUNB in Smart Agriculture
TPUNB (Narrowband Internet of Things Communication System) offers significant advantages in smart agriculture, particularly in data transmission, device connectivity, and remote monitoring. As a domestically developed technology, TPUNB plays a crucial role in providing stable, low-power communication solutions for large-scale agricultural sensor networks.
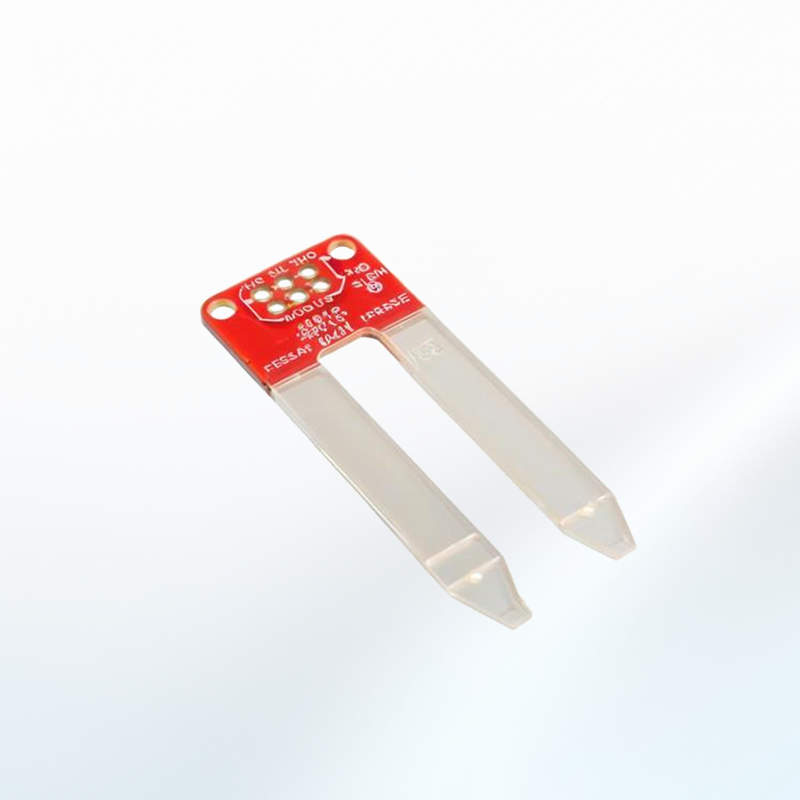
Soil Moisture Sensor
Soil moisture sensors measure the water content in the soil, providing crucial data for irrigation management.
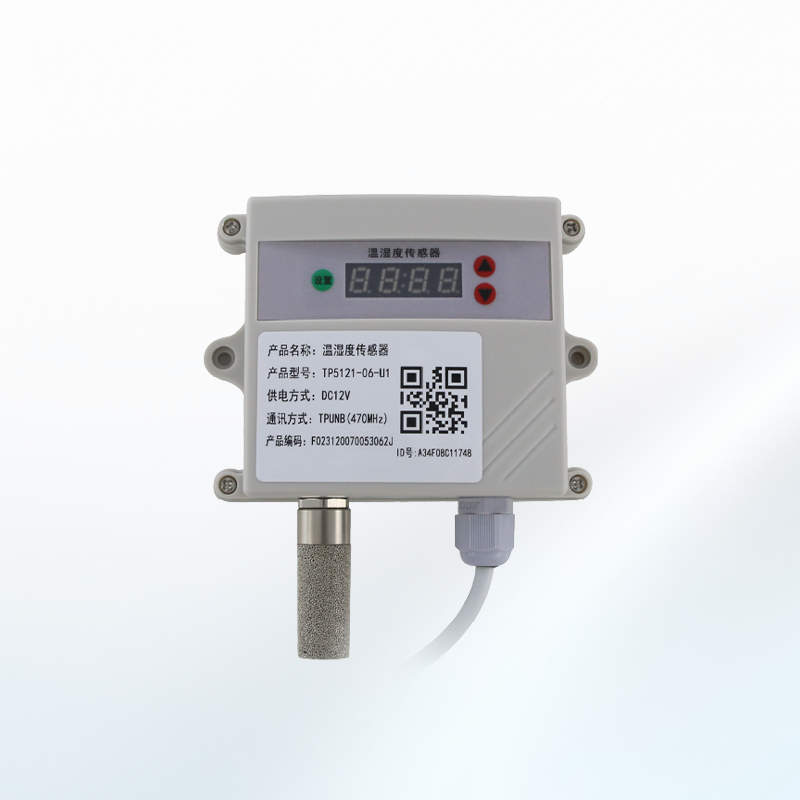

Temperature Sensor
Temperature and humidity sensors are essential for monitoring environmental conditions in agriculture.
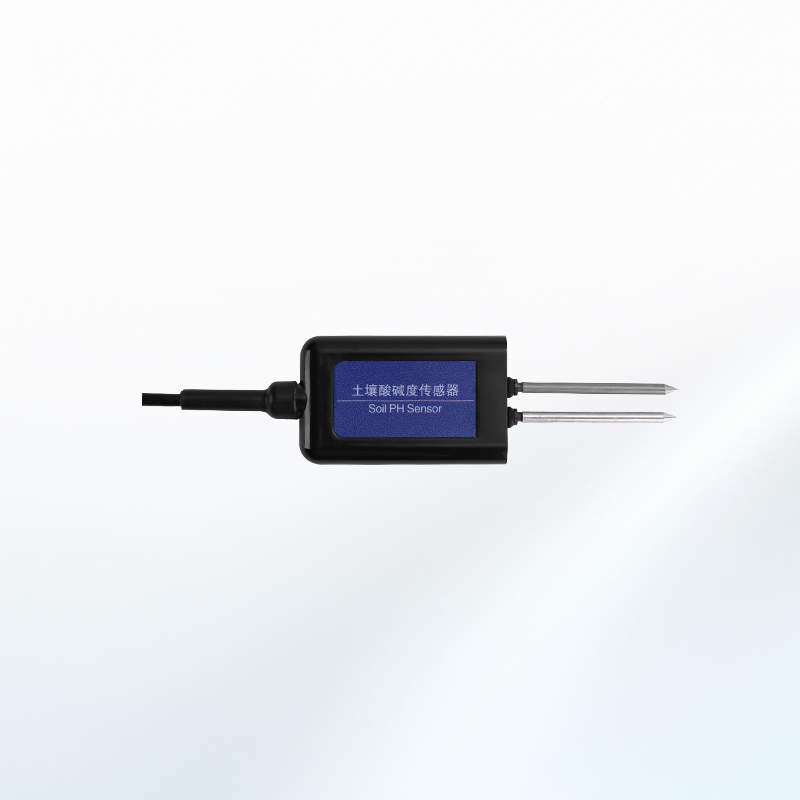

pH Sensor
pH sensors measure the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, which is crucial for nutrient availability and overall plant health.
